Fox-pro Programming 2.6
Foxpro for MS-DOS - Basic FoxPro 2.6 Commands
|
- FoxPro is SEMI-RDBMS
- Unlike other RDBMS systems, in FoxPro each database can contain only one table.
- Hence, the single table is called as database in this tutorial
In FoxPro, first four characters of any command is enough to execute
For e.g.:- crea ==> create
1. TO OPEN A DATABASE:
Syn:
use <dbname>
Ex:
use book
2.TO CLOSE THE DATABASE:
Use
To close the current opened database.
Close all
To close the all opened database.
3. To CREATE NEW DATABASE:
Syn:
crea <dbname>
crea <dbname>
create <dbname>
Ex:
crea book
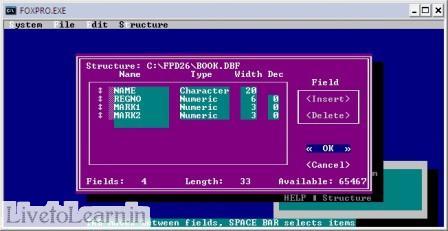
4. To Modify Structure of the Database:
Modify structure
(Or)
Modi stru
5. To add new records in database
Append is used to add the new record.
Syn:
append
[Blank]
[From <dbname>]
Ex
Append
Append Blank
- To add blank records.
Append from first.dbf
- To add the records from FIRST.DBF to SECOND.DBF
- Same Structure is required for these databases
Append Blank
- To add blank records.
Append from first.dbf
- To add the records from FIRST.DBF to SECOND.DBF
- Same Structure is required for these databases
6. To display the records in the current database
Used to display the particular record.
Syn:
Display
[All]
[Structure]
[Status]
[Memory]
Ex:
Display
Display All
Display All Records in page wise.
Display All
Display All Records in page wise.
7. To Display the structure of the database:
Display Structure
8. To display the status of the set commands:
Display Status
9. To display the status of the system memory variables.
Display Memory
10. To view the status bar
Set stat on
11. To edit records
EDIT
- It list all the records one by one for editing.
Any one of the record can be edited using 'FOR' as below
EDIT FOR empname = "LEELA"
EDIT FOR rollno = 103
12. To delete records
DELETE
- To delete current record
DELETE NEXT 4
- To delete next 4 records
After using the delete command the records marked with * (asterisk) mark, i.e., marked for deletion.
RECALL
- It is used to recover the deleted records.
e.g. RECALL
RECALL NEXT 4
PACK
- To delete the records permanently. It is used after the delete command.
BLANK
- It can be used to empty the record instead of deleting.
13. To delete all the records in the current database
ZAP
14. Navigation with Records
GO or GOTO both do the same things in Foxpro.
GO TOP
Used to move the record pointer at the first record.
GO BOTTOM:
Used to move the record point at the last record.
Go
To go to a particular record
Syn:- GO <recordno>
Eg:- GO 8
Go to record 8
SKIP
- To skip number of records
e.g. To skip 3 records - SKIP 3
15. To List the records
LIST - To list the records in screen, not in window
It can be used with condition as below:
LIST for val(price) > 100
LIST itemname, price+20
- This command lists item name with price rupees 20 added. The changes are applied only to the view, it not saved in database.
LIST product, price*2
- price is multiplied with 2.
16. To view the records as manipulatable view
BROWSE - To browse the records
BROWSE NOEDIT - To browse the records in read only view, The records can be marked for deletion using Ctrl + T shortcut
BROWSE NODELETE - To avoid deleting while browsing the records
17. To display current record number
?RECNO()
18. To display the dbf files in the current directory
DIR
19. Hide or Show heading in list view
SET HEADINGS OFF
SET HEADINGS ON
20. Printing
SET PRINT ON
- This command sends the out put to printer
- To stop this use the command SET PRINT OFF
SET PRINTER TO LPT1
- To set the output printing port to LPT1
21. Handling date and date format
To display current system date
?DATE()
To set century on to display year in 4 digits.
SET CENTURY ON
SET CENTURY OFF
To set date format
dd/mm/yyyy => SET DATE BRIT
mm/dd/yyy => SET DATE AMERICA
yyyy/mm/dd => SET DATE JAPAN
22. Replace command
To replace the content of the specified field in the database table. i.e., This command can be used to remove the data in the particular field (nullifying / empty a field)
e.g.
REPLACE fieldname WITH ""
- To replace with null value
REPLACE fieldname WITH { / / }
- To replace the date field with null value
REPLACE ALL QUANTITY WITH 0
- Replaces the data in the quatity fied with 0 in all the records.
REPLACE ALL PRICE WITH PRICE+50
- Adds 50 to the price field.
23. Blank
To blank some or all the fields in the current record.
BLANK
- To blank all the fields in the current record
BLANK FIELDS <field1>, <field>
- To blank specified fields in the current record
PROGRAM
A Program is a set of instructions used to achieve the desired output.
A Program is a set of instructions used to achieve the desired output.
To create new program or to edit the existing one.
MODI COMM
OR MODIFY COMMAND <PRGRAM_NAME>
NOTE command
If ignore the particular line or command, NOTE can be used at the beginning of that line.
Comment Line
To add comments to the right of the Programming code , use &&
Clear All Command
This command is used to closes all databases files and releases all active memory variables, arrays menus or popup.
Input / Output command
? | ?? | ??? [expr1?]
? - To print the expression in new line
?? - To print the expression in the same line
??? - The Output will going to the printer
Example:
? "Hellow!"
Sample Program
NOTE prg for just print something on the screen
Clear && To Clear the Screen or previous outputs
?"Welcome"
?"Hellow!"
?? " World...!"
??? "Thank you”
Writing Programs
* FoxPro has powerful built-in editor for writing and editing.
* It can be invoked from the command window by using the MODIFY COMMAND.
Syntax:
MODIFY COMMAND <prenames>
Example:
Modify Command journal
(This program will automatically save with the extension .PRG)
Press CTRL + W - To save and close the program window
Executing Program
Programs can be executed by DO command.
Syntax:
DO <prgname>
Example:
Do journal
When compile the executed file the FoxPro creates an object code program with .FXP extension. If there are any errors, creates a file an .ERR extension.
INPUT command
It is used to accept Numeric input from the user and store it into a memory variable.
Syntax:
INPUT [<char exp>] TO <memvar>
Example:
Store 0 to eno
INPUT "Enter your Enrollment No : " TO eno
? Eno
ACCEPT command
It is used to accept character input from the user and store it into a memory variable.
Syntax:
ACCEPT [<char exp>] TO <memvar>
Example:
Store space (15) to NAM
ACCEPT "Enter the Name: " to NAM
? "Entered name:” NAM
Example 2
clear
SET TALK OFF
Accept "Enter your nane :" to nam
Input "enter your Age : " to age
Accept " enter your city :" to cit
Accept "Enter your Mail id : " to mail
? "******************************************"
? "NAME :: " ,nam
? "AGE :: " ,age
? "CITY :: " ,cit
? "MAIL ID:: " ,mail
? "******************************************"
Setting/restoring the environment
Every FoxPro program includes all commands required to establish the working environment and restore it to its prior state before the program terminates execution. This is achieved by issuing some set.
Set notify on/off
Enables the display of certain system messages.
Set talk window
Directors the display of system messages to an user-defined window instead of the system window. Sets notify should be ON.
Set deleted on/off
Processes records marked for deletion.
MODI COMM
OR MODIFY COMMAND <PRGRAM_NAME>
NOTE command
If ignore the particular line or command, NOTE can be used at the beginning of that line.
Comment Line
To add comments to the right of the Programming code , use &&
Clear All Command
This command is used to closes all databases files and releases all active memory variables, arrays menus or popup.
Input / Output command
? | ?? | ??? [expr1?]
? - To print the expression in new line
?? - To print the expression in the same line
??? - The Output will going to the printer
Example:
? "Hellow!"
Sample Program
NOTE prg for just print something on the screen
Clear && To Clear the Screen or previous outputs
?"Welcome"
?"Hellow!"
?? " World...!"
??? "Thank you”
Writing Programs
* FoxPro has powerful built-in editor for writing and editing.
* It can be invoked from the command window by using the MODIFY COMMAND.
Syntax:
MODIFY COMMAND <prenames>
Example:
Modify Command journal
(This program will automatically save with the extension .PRG)
Press CTRL + W - To save and close the program window
Executing Program
Programs can be executed by DO command.
Syntax:
DO <prgname>
Example:
Do journal
When compile the executed file the FoxPro creates an object code program with .FXP extension. If there are any errors, creates a file an .ERR extension.
INPUT command
It is used to accept Numeric input from the user and store it into a memory variable.
Syntax:
INPUT [<char exp>] TO <memvar>
Example:
Store 0 to eno
INPUT "Enter your Enrollment No : " TO eno
? Eno
ACCEPT command
It is used to accept character input from the user and store it into a memory variable.
Syntax:
ACCEPT [<char exp>] TO <memvar>
Example:
Store space (15) to NAM
ACCEPT "Enter the Name: " to NAM
? "Entered name:” NAM
Example 2
clear
SET TALK OFF
Accept "Enter your nane :" to nam
Input "enter your Age : " to age
Accept " enter your city :" to cit
Accept "Enter your Mail id : " to mail
? "******************************************"
? "NAME :: " ,nam
? "AGE :: " ,age
? "CITY :: " ,cit
? "MAIL ID:: " ,mail
? "******************************************"
Setting/restoring the environment
Every FoxPro program includes all commands required to establish the working environment and restore it to its prior state before the program terminates execution. This is achieved by issuing some set.
Set notify on/off
Enables the display of certain system messages.
Set talk window
Directors the display of system messages to an user-defined window instead of the system window. Sets notify should be ON.
Set deleted on/off
Processes records marked for deletion.
Input and Output Statements in Foxpro
Input and output in foxpro
As we already know that data can be entered into tables through the APPEND/BROWSE commands. Data entry for tables can also be done through programs. There arises a need to display and accept information in a formatted way.
The @…say command is used to place data at a particular screen location and to display data stored in fields or memory variables. The @…get commands is used to retrieve data.
Displaying data
@…say command: -
Syntax: -
@<Row, columns>SAY<expr>
[Function<exprC1>]
[Picture<expr2>]
[size<exprn],<exprn2>]
[font<exprC3>[,<exprN3]]
[STYLE, exprC4>]
Example:-
@2, 10 say “hello welcome to FoxPro”
As we already know that data can be entered into tables through the APPEND/BROWSE commands. Data entry for tables can also be done through programs. There arises a need to display and accept information in a formatted way.
The @…say command is used to place data at a particular screen location and to display data stored in fields or memory variables. The @…get commands is used to retrieve data.
Displaying data
@…say command: -
Syntax: -
@<Row, columns>SAY<expr>
[Function<exprC1>]
[Picture<expr2>]
[size<exprn],<exprn2>]
[font<exprC3>[,<exprN3]]
[STYLE, exprC4>]
Example:-
@2, 10 say “hello welcome to FoxPro”
Syntax:
Input
@row,column | say <char_exp> get <mem_var>
Output
@row ,column | say <char_exp> get <mem_var>
Clear
@row, column to row, column clear
Clear all
Ex
@5, 5 clear to 20, 20
Box Command
@row1, column1 to row2, column 2
Picture clause
PICTURE clause is used to control of display or the information to be accepted.
@..SAY...GETS PICTURE CODES:
A - Allows only alphabets
9 - Allows only digits, signs for numeric data
N - Allows Letters and Digits
# - Allows Only Digits, Blanks and Signs
X - Allows any Character
L - Allows any Logical Data T, t, F, f, Y, y, N, n
Y - Allows Only Y, y, N, n
! - Converts letters into uppercase.
* - Displays asterisk in place of leading zeros.
, - Display the comma
. - Display the decimal Point.
Function Clause
You can include the function clause, the picture clause or both to control how<expr> is displayed or printed. A function clause affects the entire expression. It contains only the following function code.
Function code & Purpose
B Left – justifies numeric data within the display region.
Example:
Clear
Store 2750 to num
@5,20 say num
@6,20 say num function “B”
C Cr is displayed after a positive number to indicate a credit. Can be used with numeric data only.
Example:-
Clear
Store 15432.00 to amt
@5,20 say amt
@6,20 say amt function “c”
D Uses the current set DATE format.
Example:-
Clear
Store 230801 to num
Store “foxproprograming” to tit
@5,20 say num function “D”
@6,20 say tit function “D”
E Edits date type data as British date
Example:-
Clear
Store 230904 to num
@6,20 say num function “E”
T Trim leading and trailing blanks from<expr>
Example:-
Clear
@5,20 ”fox” to tit
@6,20 say tit function “T”
X DB is displayed after negative numbers to indicate a debit. used only with numberic data.
Example:-
Clear
Store -15432.00 to amt
@5,20 say amt
@6,20 say amt function “X”
Input
@row,column | say <char_exp> get <mem_var>
Output
@row ,column | say <char_exp> get <mem_var>
Clear
@row, column to row, column clear
Clear all
Ex
@5, 5 clear to 20, 20
Box Command
@row1, column1 to row2, column 2
Picture clause
PICTURE clause is used to control of display or the information to be accepted.
@..SAY...GETS PICTURE CODES:
A - Allows only alphabets
9 - Allows only digits, signs for numeric data
N - Allows Letters and Digits
# - Allows Only Digits, Blanks and Signs
X - Allows any Character
L - Allows any Logical Data T, t, F, f, Y, y, N, n
Y - Allows Only Y, y, N, n
! - Converts letters into uppercase.
* - Displays asterisk in place of leading zeros.
, - Display the comma
. - Display the decimal Point.
Function Clause
You can include the function clause, the picture clause or both to control how<expr> is displayed or printed. A function clause affects the entire expression. It contains only the following function code.
Function code & Purpose
B Left – justifies numeric data within the display region.
Example:
Clear
Store 2750 to num
@5,20 say num
@6,20 say num function “B”
C Cr is displayed after a positive number to indicate a credit. Can be used with numeric data only.
Example:-
Clear
Store 15432.00 to amt
@5,20 say amt
@6,20 say amt function “c”
D Uses the current set DATE format.
Example:-
Clear
Store 230801 to num
Store “foxproprograming” to tit
@5,20 say num function “D”
@6,20 say tit function “D”
E Edits date type data as British date
Example:-
Clear
Store 230904 to num
@6,20 say num function “E”
T Trim leading and trailing blanks from<expr>
Example:-
Clear
@5,20 ”fox” to tit
@6,20 say tit function “T”
X DB is displayed after negative numbers to indicate a debit. used only with numberic data.
Example:-
Clear
Store -15432.00 to amt
@5,20 say amt
@6,20 say amt function “X”
Z <expr> is displayed as all blanks if its numeric
value is 0. used only with numeric data.
Example:
Clear
Store o to amt
@5,20 say amt
@6,20 say amt function “z”
value is 0. used only with numeric data.
Example:
Clear
Store o to amt
@5,20 say amt
@6,20 say amt function “z”
( Encloses negative numbers in parentheses. Used only with numeric data.
Example:-
Clear
Store –755 to amt
@5,20 say amt
@6,20 say amt function “(“
Example:-
Clear
Store –755 to amt
@5,20 say amt
@6,20 say amt function “(“
! Converts alphabetic characters to upper-case used with character data-only
Example:-
Clear
Store “foxpro programming” to tit
@6,20 say tit function “!”
Example:-
Clear
Store “foxpro programming” to tit
@6,20 say tit function “!”
^ Displays numeric data using scientific notation. Used with numeric data only.
Example:-
Clear
Store 75815 to amt
@6,20 say amt function “^”
Example:-
Clear
Store 75815 to amt
@6,20 say amt function “^”
$
Displays data in currently format. the currency symbol appears before or after the field value depending on the current setting of set currency. used with numeric data only.
Example:-
Clear
Store 75815 to amt
@6,20 say amt function “$”
Picture expression can include the following characters:-
Displays data in currently format. the currency symbol appears before or after the field value depending on the current setting of set currency. used with numeric data only.
Example:-
Clear
Store 75815 to amt
@6,20 say amt function “$”
Picture expression can include the following characters:-
X Allows any character.
Y Allows logical Y, y, N and n only. Converts y and n to Y and N, respectively.
! Displays the current currency symbol specified by set currency. By default, the symbol is placed immediately before or after the field.
* Asterisks are displayed in front of the numeric value. Use with a dollar sign $ for check protection.
. A decimal point specifies the decimal point position.
, A comma is used to specifies digits to the left of the decimal point.
! Displays the current currency symbol specified by set currency. By default, the symbol is placed immediately before or after the field.
* Asterisks are displayed in front of the numeric value. Use with a dollar sign $ for check protection.
. A decimal point specifies the decimal point position.
, A comma is used to specifies digits to the left of the decimal point.
Control Structures in Foxpro
Control Structures
IF statement
If Condition is True Executed and then False Not Executed.
Syntax
If (condition) then
Statement-1
End if
Example
clear
mark =0
@5,5 say " Enter the Mark : " get mark RANGE 0,100
Read
If mark >=40 Then
@10,10 say " You have PASS"
Endif
IF statement
If Condition is True Executed and then False Not Executed.
Syntax
If (condition) then
Statement-1
End if
Example
clear
mark =0
@5,5 say " Enter the Mark : " get mark RANGE 0,100
Read
If mark >=40 Then
@10,10 say " You have PASS"
Endif
If….else….endif:-
The commands between if…..end if will be executed only if condition is satisfied, otherwise the next statement is executed. For every if there must be an end if. Every is matched with the nearest unmatched if.
Syntax:-
If<condition>
<Command sequence-1>
Else
<Command sequence-2>
End if
The commands between if…..end if will be executed only if condition is satisfied, otherwise the next statement is executed. For every if there must be an end if. Every is matched with the nearest unmatched if.
Syntax:-
If<condition>
<Command sequence-1>
Else
<Command sequence-2>
End if
Command sequence –1 will be executed if a condition is true, if condition is false command sequence-2 will be executed. Control falls to the next statement in either case, if program I still in execution.
Example 2
clear
Store 0 to x,y
@5, 5 say " Enter the First value: " get x
@7,5 say " Enter the Second value: " get y
Read
IF x > y Then
@10, 10 say str(x) + “is Greater than” + ltrim (str(y))
Else
@10, 10 say str(x) + " is lesser than " + ltrim (str(y))
Endif
Example 3
clear
Store space(1) to x,ch
@5, 5 say " Enter any Alphabet: " get x
Read
ch =chr(asc(x) +32) && To convert Upper into Lower
IF ch="a" .or. ch="e" .or. ch="i" .or. ch="o" .or. ch="u" then
@10,10 say ch + " is a VOWEL "
Else
@10,10 say ch + " is a CONSONANT"
Endif
clear
Store 0 to x,y
@5, 5 say " Enter the First value: " get x
@7,5 say " Enter the Second value: " get y
Read
IF x > y Then
@10, 10 say str(x) + “is Greater than” + ltrim (str(y))
Else
@10, 10 say str(x) + " is lesser than " + ltrim (str(y))
Endif
Example 3
clear
Store space(1) to x,ch
@5, 5 say " Enter any Alphabet: " get x
Read
ch =chr(asc(x) +32) && To convert Upper into Lower
IF ch="a" .or. ch="e" .or. ch="i" .or. ch="o" .or. ch="u" then
@10,10 say ch + " is a VOWEL "
Else
@10,10 say ch + " is a CONSONANT"
Endif
NESTED IF: (IF within IF)
clear
store 0 to x,y,z
@5,5 say " Enter No1 : " get x
@7,5 say " Enter No2 : " get y
@9,5 say " Enter No3 : " get z
Read
If x > y then
IF x>z then
@ 15,5 say " X is Greater than y and z"
Else
@15,5 say "X is Greater than Y and Lesser than Z"
Endif
Else
IF Y>Z then
@ 15,5 say " Y is Greater than X and Z"
Else
@15,5 say "Y is Greater than X but not Z"
Endif
Endif
DO CASE
Case Commands are used to check for a specified condition
Syntax:
DO Case
Case <variable> = <value>
Statement -1
Case <variable> = <value>
Statement -2
Otheriwse
Statement -3
End Case
Example:
clear
store 0 to day
@5,5 say " Enter any number from 1 to 7 " get day
Read
DO CASE
case day = 1
@10,10 say "SUNDAY"
case day = 2
@10,10 say "MONDAY"
case day = 3
@10,10 say "TUESDAY"
case day = 4
@10,10 say "WEDNESDAY"
case day = 5
@10,10 say "THURSDAY"
case day = 6
@10,10 say "FRIDAY"
case day = 7
@10,10 say "SATURDAY"
OTHERWISE
@10,10 SAy "Invalid Input"
EndCase
FOR LOOP
clear
store 0 to x,y,z
@5,5 say " Enter No1 : " get x
@7,5 say " Enter No2 : " get y
@9,5 say " Enter No3 : " get z
Read
If x > y then
IF x>z then
@ 15,5 say " X is Greater than y and z"
Else
@15,5 say "X is Greater than Y and Lesser than Z"
Endif
Else
IF Y>Z then
@ 15,5 say " Y is Greater than X and Z"
Else
@15,5 say "Y is Greater than X but not Z"
Endif
Endif
DO CASE
Case Commands are used to check for a specified condition
Syntax:
DO Case
Case <variable> = <value>
Statement -1
Case <variable> = <value>
Statement -2
Otheriwse
Statement -3
End Case
Example:
clear
store 0 to day
@5,5 say " Enter any number from 1 to 7 " get day
Read
DO CASE
case day = 1
@10,10 say "SUNDAY"
case day = 2
@10,10 say "MONDAY"
case day = 3
@10,10 say "TUESDAY"
case day = 4
@10,10 say "WEDNESDAY"
case day = 5
@10,10 say "THURSDAY"
case day = 6
@10,10 say "FRIDAY"
case day = 7
@10,10 say "SATURDAY"
OTHERWISE
@10,10 SAy "Invalid Input"
EndCase
FOR LOOP
- To repeatedly execute a series of lines in a Program.
- The lines of code b/w FOR and ENDOFR will be executed until the memory variable is equal to the final condition specified.
- Default STEP value is 1.
Syntax
FOR <memvar> = <initial value> TO <final value> STEP <no>
................
................
ENDFOR
Example: 1
CLEAR
FOR I = 1 TO 10
? I
EndFor
Example: 2
To print the EVEN nos from 2 to 50
CLEAR
FOR I = 2 TO 50 STEP 2
? I
EndFor
FOR <memvar> = <initial value> TO <final value> STEP <no>
................
................
ENDFOR
Example: 1
CLEAR
FOR I = 1 TO 10
? I
EndFor
Example: 2
To print the EVEN nos from 2 to 50
CLEAR
FOR I = 2 TO 50 STEP 2
? I
EndFor
This is an example of simple navigation menu programming in Foxpro 2.6
- set talk off
- set stat off
- set scor off
- set cent on
- set date brit
- do whil .t.
- clea
- @5,20 to 19,45 doub
- @6,25 say "MAIN MENU"
- @7,21 to 7,44 doub
- k=0
- @ 9,25 prompt "DATA ENTRY"
- @11,25 prompt "REPORT PRINTING"
- @13,25 prompt "PROCESS"
- @15,25 prompt "EXIT"
- @17,25 prompt "QUIT to SYSTEM"
- menu to k
- do case
- case k=1
- do dataent
- case k=2
- do repoprn
- case k=3
- * do proces
- case k=4
- exit
- case k=5
- clos all
- clea all
- quit
- otherwise
- loop
- endcase
- enddo
- clos all
- clea all
- proce dataent
- do whil .t.
- clea
- @5,20 to 19,55 doub
- @6,30 say "DATA ENTRY MENU"
- @7,21 to 7,54
- k1=0
- @ 9,25 prompt "1. STUDENT"
- @11,25 prompt "2. STAFF"
- @13,25 prompt "3. FEES "
- @15,25 prompt "4. COURSES"
- @17,25 prompt "RETURN TO MAINMENU"
- menu to k1
- do case
- case k1=1
- do stud
- case k1=2
- do staff
- case k1=3
- do fees
- case k1=4
- do course
- case k1=5
- exit
- otherwise
- loop
- endcase
- enddo
- clos all
- return
- proce repoprn
- do whil .t.
- clea
- @5,20 to 19,55 doub
- @6,30 say "REPORT MENU"
- @7,21 to 7,54
- k1=0
- @ 9,25 prompt "Report 1"
- @11,25 prompt "Report 2"
- @13,25 prompt "Report 3"
- @15,25 prompt "Report 4"
- @17,25 prompt "Return to Mainmenu"
- menu to k2
- do case
- case k2=1
- do fmainprn
- case k2=2
- do fothrprn
- case k2=3
- do mainprn
- case k2=4
- do othrprn
- case k2=5
- exit
- otherwise
- loop
- endcase
- enddo
- clos all
- return


Simple Journal Entry program
All-in-one web based software for Apartment management
Simple Ledger creation & Posting Program
Aviva iLife: Online Term Plan with Real Quick, Easy & Affordable!
Trial Balance Program
100% Pure Gold From Bullion India Delivery @ Door step, Invest Now